Learn about the pros and cons of different blasting media types and which projects you should use them for -- including sand blasting, vapor blasting, soda blasting, and dustless blasting.
What is Abrasive?
Abrasive (also called media or abrasive blasting media) is added to the blast pot and sometimes mixed with water depending on the application. When abrasive blasting, you propel this mixture towards a surface at high speed, to remove paint, rust, and other coatings.
Types of Abrasive
Dustless Blasting or other sandblasting equipment allows you to use a wide variety of abrasives, either wet or dry. For wet blasting, any abrasive that sinks in water and is not water soluble can be used. However, abrasives that are dirty or have a very inconsistent particle size can cause problems, such as sputtering or clogging of the machine.
Here are just some of the abrasives that you can use with the Dustless Blaster:
- Recycled bottle glass
- Garnet
- Blast sand
- Sugar sand
- Coal slag
- Copper slag
- Glass beads
- Sodium Bicarbonate
- Walnut shell
- Corn cob
Our favorite abrasive is recycled bottle glass, because it's clean, inexpensive, environmentally friendly, and suited for a wide variety of jobs. Sometimes different abrasives are available simply based on geography.
A common question we get is "Can I use play sand?" The answer is NO. Play sand is not an industrial product, so it's not controlled and graded the way abrasives are. It won't behave predictably in your equipment, and you could wind up in loads of legal trouble, from the EPA to local municipalities. Most bags of play sand are explicitly marked "Not to be used for sandblasting".
Where can I buy media?
You can purchase blasting media at the Dustless Blasting Parts Store and have it shipped to you! We sell the 40/70 recycled glass for $10 per 50lb bag.
If you'd prefer to save on shipping costs, you can also purchase media from a local supplier.
Abrasive Shape
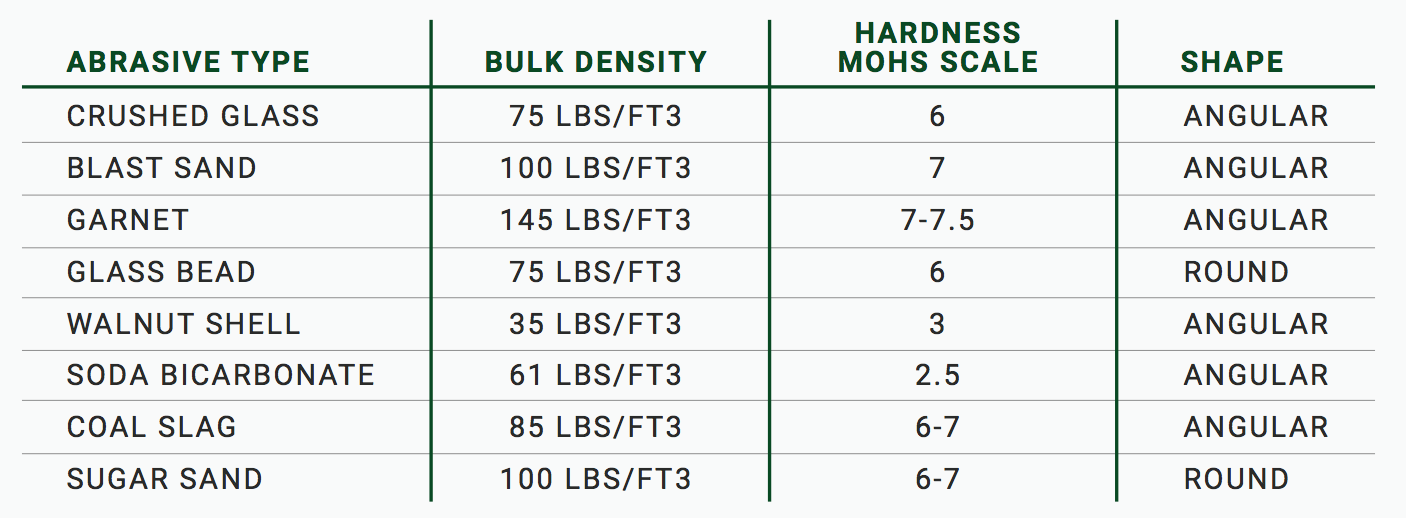
Basically, there are two different shapes: angular which has sharp edges, and round with no edges.

Angular abrasive has sharp edges which will cut into the substrate, leaving an anchor profile for the new finish to stick to. Examples of angular shaped media would be crushed glass, slags and garnet abrasives to name a few.
Round media is used mainly for cleaning or stripping while leaving the surface smooth. It will not rough up the surface or leave an anchor profile. Examples of round media would be glass beads, sugar sand and plastic pellets.
An anchor profile is a fancy way of describing the rough surface created during the blasting process. These peaks and valleys are usually measured in mils (1/1000 of an inch). One of the main causes of premature coating failure is an insufficient anchor profile. It's a good idea to understand from the customer what he/she expects when you are done. Some people prefer an anchor profile, while others will want a smoother surface.
For example, if you are stripping a car to be repainted, you'll probably want to leave an anchor profile for the new paint to adhere to. If you are simply cleaning calcium deposits from a pool — which will not be repainted — leaving a profile is unnecessary.
Abrasive Size
Most abrasive is measured with mesh size. During production, it gets shaken through various screens. These screens might have as little as 20 holes per square inch, or as many as 100. This means that 40/70 glass fits through the 40–70 holes per square inch screens.
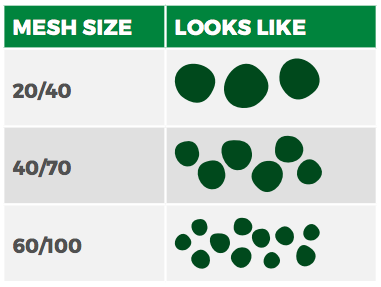
20/40 glass is coarser than 40/70, and 60/100 glass is finer.
A common misconception is that the coarser glass will help you get through a job faster. It is true that 20/40 glass is slightly more aggressive than 40/70. However, because it's so coarse, you're only getting half as many particles of glass in the same size bag. You'll end up using twice as many bags to get the job done, which is not only expensive, but inefficient! It's a much better idea to increase abrasive density if you want to complete the job faster.
Abrasive Weight/Density
Understanding the weight or bulk density of the media you are using will also help decide which is best for the process. The heavier the media, the more impact it has on the surface you are blasting.
Imagine a golf ball and a ping pong ball. They are the same shape and size, but the golf ball is more dense. If you threw them at someone, the golf ball would hurt a lot more.
Crushed glass has a bulk density of 75-80 lbs per cubic foot— while garnet weighs around 145 lbs per cubic foot. So, the two abrasives at the same mesh size and blast pressure will have different results. A 40/70 crushed glass will be more “gentle” on the surface than the same mesh size of garnet at the same blast pressure.
The harder and heavier the abrasive is, the rougher the profile will be. Using larger, more coarse abrasives will decrease the run time in your machine. For example, if you are blasting with 40/70 crushed glass and decide to use a larger mesh size of 20/40 you will notice a decrease in run time. If both bags of abrasive are 50 lbs, there are fewer particles in the 20/40 mesh size bag than the 40/70. A larger mesh size will be more aggressive so it will have more of an impact to the surface you are blasting.
Comparison Chart
There isn’t necessarily a right or wrong way to remove a coating. The deciding factors would be speed and end result of the substrate you are stripping. Understanding the impact of different abrasives will help in deciding the best media for the job. The following chart will explain the characteristics of various media types.
Examples
To see examples of real-life blasting jobs and what abrasive you should use for them, download our PDF guidebook on Choosing the Right Abrasive!
In Conclusion
Choosing an abrasive is like choosing sandpaper for a project. More coarse sandpaper like 60 grit or 100 grit will strip quicker and have a rougher surface, while finer mesh like 400 or 1000 grit will be slower and have a smoother finish. Finer meshed abrasives are great for softer substrates like fiberglass, concrete and wood, while larger mesh abrasives work best for thick steel or thick coatings.
To sum it up, 40/70 crushed glass is a great general, all around blasting abrasive. If crushed glass is struggling to remove a coating then switching to a heavier abrasive like garnet will work better. Just determine what abrasive the substrate can handle and the thickness or toughness of the coating you are stripping.
Other factors that affect your results
We've covered how abrasive choice can affect your blasting, but you should also think about:
Air Pressure: Air pressure or PSI is how hard we are throwing the abrasive. The harder the substrate and coating, the more aggressive you will want to be. Learn more about choosing the right blast pressure here.
Distance from the surface you are blasting: This is very simple and will come naturally. The further from the surface you are blasting the greater the energy will dissipate. For example cleaning graffiti from a wall, you might be 2-5 feet away from the surface. Removing 80 mil of tank liner you might only be 4-10 inches from the surface. See how standoff distance affects the blast pattern in the nozzle control video.
Reclaiming Media
We often get the question "Can I reclaim or reuse blast media?"
Crushed glass is the most commonly used media in the Dustless Blaster, and it's generally not worth reclaiming. Because the glass particles shatter upon impact, they will actually end up being smaller than 40/70 after they have been used. The glass is only $10 per 50lb bag, so it's usually not worth the effort to gather, clean, and re-sift the media.
That being said, other abrasive such as glass or plastic bead are more expensive, and may be worth reclaiming, as long as they don't shatter on impact. In this video, one of our business owners used a vacuum to reclaim and reuse glass bead he used on a pool tile line.
Helpful Guides
Choosing the Right Abrasive (PDF Guidebook)
Abrasive Characteristics (Reference Sheet)
Main Levels of Surface Preparation (Reference Sheet)
Tech Talk: Choosing the Right Abrasive (Video)
Didn't solve your problem? Contact tech support here or call 713-869-2227.


